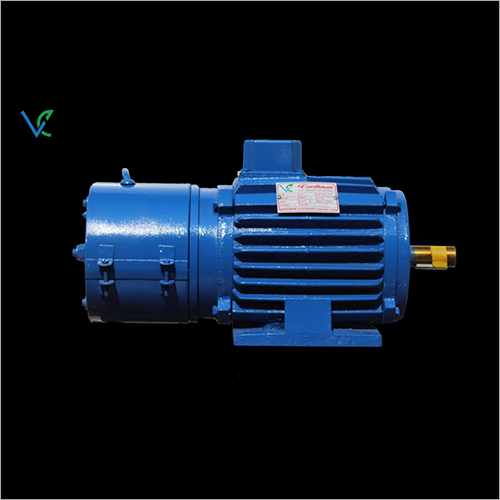
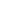
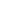
AC Brake Motor
Product Details:
- Pressure High Pressure
- Product Type Other
- Phase Three Phase
- Starting Type Electric Start
- Click to View more
AC Brake Motor Price And Quantity
- 1 Unit
AC Brake Motor Product Specifications
- High Pressure
- Three Phase
- Electric Start
- Other
AC Brake Motor Trade Information
- 10-15 Days
- All India
Product Description
Here are some essential characteristics and parts of an AC braking motor:
2. Brake Mechanism: The brake mechanism, which is part of the motor, is what causes the vehicle to brake. Typically, the brake system uses a spring-applied, electrically released design. The brake is removed when power is provided to the brake coil, allowing the motor to turn. The motor stops or holds its position when the power is turned off thanks to the brake being activated.
3. The electromagnetic component known as the brake coil manages the engagement and disengagement of the brake. When the brake is released, it is energised; when the brake is engaged, it is de-energized.
4. Brake Disc or Brake Drum: The brake system makes contact with the brake disc or brake drum to halt the rotation of the motor. The braking force is produced by friction between the disc or drum and the brake mechanism.
5. Relays, contactors, and motor starters are some of the parts of an AC brake motor's control circuit that provide the necessary electrical connections and control signals to energise or de-energize the brake coil.
The following benefits of using AC braking motors in various applications:
- Rapid and exact stopping: The integrated brake system makes it possible to quickly and precisely halt the motor's spinning, which enhances safety and productivity.
- Holding torque: When the brake is applied, AC brake motors can produce holding torque, which enables them to hold a weight in place without the use of any extra devices.
- Versatility: AC brake motors are excellent for a variety of industrial applications since they come in a variety of sizes, power ratings, and braking torque options.
When choosing an AC brake motor, it is crucial to take into account the particular requirements of the application, such as the necessary braking torque, duty cycle, and motor speed. Additionally, to guarantee the dependable operation and lifespan of the motor and brake system, correct installation, maintenance, and adherence to safety regulations are vital.
An electric motor that integrates a brake system for controlled stopping and holding torque is known as an AC brake motor. It is frequently utilised in applications that call for accurate rotational motion halting and holding and offers improved safety and performance.
FAQ
1. How do AC brake motors function?
Ans - A mechanical brake system is used by an alternating current motor known as an AC brake motor to provide precise control over the motor's output speed. Usually, a motor is coupled to an electronic control system that manages the motor's torque and speed. The mechanical brake system is also used by the AC brake motor to produce a braking force and swiftly stop the motor's rotation when the power source is withdrawn.
2. What parts of an AC braking motor are there?
Ans - An electric motor, a brake system, an electronic control unit, and a mechanical connection are the primary elements of an AC brake motor. When the control unit instructs the braking system to activate, the brake system is in charge of giving a controlled stop for the motor, which is powered by the electric motor. The mechanical linkage, which connects the brake system to the electric motor and regulates how much force is produced by the brake system, is the last component.
3. What advantages can AC brake motors offer?
Ans - Applications that ask for precise control of the motor's output speed frequently use AC braking motors. The motor may be started and stopped gradually thanks to the system, which lessens the strain on the system. Furthermore, even when exposed to sharp temperature changes, the system can maintain accurate control over the motor output speed.
4. How frequently should a braking motor for an AC unit be serviced?
Ans - In order to make sure the system is performing at its best, it is advised that an AC brake motor be maintained once a year. All connections inside the system should be cleaned and inspected, and any worn parts or components should be replaced.
5. Should I take any special safety measures when working with an AC brake motor?
Ans - Yes, when working with an AC brake motor, it is crucial to take a number of safety measures. When maintaining the system, appropriate protective clothing should always be worn, and insulated tools should be used. Before attempting to do any repairs or adjustments, it is also crucial to confirm that all connections to the electrical components are secure and that the motor is unplugged from the power source.